Mold Repair Services
Mold Repair Services: Expert solutions for restoring molds to optimal functionality. Precision repairs ensure prolonged lifespan and enhanced performance.
Mold Repair
What is Mold Repair?
Mold repair refers to the process of restoring molds to their original functionality or improving their performance through various repair techniques such as welding, polishing, and re-machining. This service ensures that molds remain operational and efficient, minimizing downtime and production interruptions.
Precision Injection Mold Manufacturing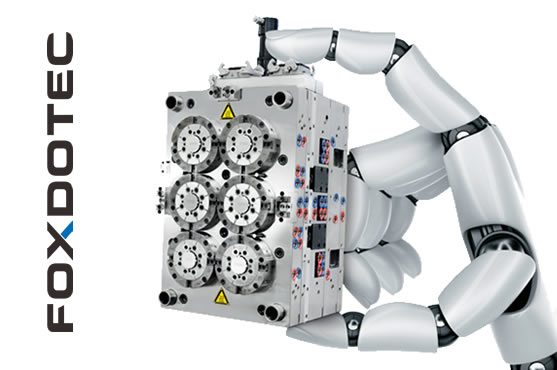


What is the process of Mold Repair?
Mold Repair Process
The process of mold repair involves several detailed steps to ensure that molds are restored to their optimal condition. Here's a comprehensive overview:
- Assessment: The first step is to assess the condition of the mold thoroughly. This involves inspecting for damage, wear, or any other issues that may affect its performance.
- Disassembly: The mold is carefully disassembled to access all components. This allows for a closer examination of individual parts and facilitates the repair process.
- Cleaning: All components of the mold are cleaned to remove any debris, residue, or contaminants. This ensures that the repair work is performed on clean surfaces, preventing further damage.
- Repair: Depending on the nature of the damage, various repair techniques may be employed. Common repair methods include welding, grinding, polishing, and machining to correct imperfections, cracks, or wear.
- Replacement: In cases where components are too damaged to be repaired, they may need to be replaced with new parts. This could include inserts, cores, or other critical elements of the mold.
- Surface Treatment: After repairs are completed, surfaces may undergo treatment to enhance durability, corrosion resistance, or improve release properties. This could involve coatings, plating, or other surface treatments.
- Assembly: Once all repairs and treatments are done, the mold components are carefully reassembled according to the original specifications. Proper alignment and fit are crucial to ensure the mold functions correctly.
- Testing and Quality Control: The repaired mold undergoes rigorous testing to ensure that it meets the required specifications and performance standards. This may involve trial runs, dimensional checks, and other quality control measures.
- Documentation: Detailed documentation of the repair process, including any modifications or adjustments made, is essential for future reference. This helps in tracking the history of the mold and planning maintenance schedules.
- Final Inspection and Delivery: Before the repaired mold is returned to production, a final inspection is conducted to verify its integrity and functionality. Once approved, the mold is delivered back to the customer for use.
By following these meticulous steps, mold repair services ensure that damaged molds are effectively restored, prolonging their lifespan and optimizing production processes.
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a computer-controlled manufacturing process that utilizes pre-programmed software to dictate the movement of machinery and tools. This technology enables the precise cutting, drilling, and shaping of materials such as metal, plastic, and wood to create intricate components with high accuracy and consistency.
Read More
Precision Grinding
Precision grinding is a manufacturing process that involves the removal of material using abrasives to achieve extremely tight tolerances and surface finishes. used to produce components with intricate shapes, precise dimensions, and smooth surfaces. Precision grinding techniques include cylindrical grinding, surface grinding, and internal grinding.
Read More
Electrical Discharge Machining
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a non-traditional machining process that utilizes electrical discharges to erode material from a workpiece. It is particularly useful for machining complex shapes and hardened materials that are difficult to machine with conventional methods. EDM can achieve high precision and surface quality.
Read MorePrecision machining and manufacturing involve the use of advanced techniques and equipment to produce highly accurate and intricate components with tight tolerances. It requires expertise in machining processes, material properties, and quality control methods to ensure the production of high-quality parts for various industries.
Key Aspects of Understanding Injection Molds
- Design Principles: Understand the principles of injection mold design, including considerations for part geometry, material flow, cooling, and ejection.
- Materials and Construction: Explore the materials commonly used in injection mold construction, such as tool steel, aluminum, and beryllium copper.
- Manufacturing Techniques: Gain insights into the manufacturing processes used to produce injection molds, including machining, EDM, and CNC milling.
- Mold Maintenance and Repair: Learn about the importance of mold maintenance and preventive maintenance schedules to ensure the longevity and performance of injection molds.
- Tooling Standards and Regulations: Familiarize yourself with industry standards and regulations related to injection mold design and manufacturing.
- Advanced Technologies: Stay informed about advancements in injection mold technology, such as rapid prototyping, additive manufacturing (3D printing), and simulation software.
- Cost Considerations: Gain insights into the cost factors associated with injection mold production and learn about strategies for cost optimization.
- Case Studies and Best Practices: Study real-world examples of successful injection mold projects across various industries.
Key Aspects of Understanding Precision Machining
- Processes and Techniques: Explore the various precision machining processes and techniques, including turning, milling, drilling, grinding, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and others.
- Materials: Learn about the different types of materials commonly machined using precision techniques, such as metals (e.g., aluminum, steel, titanium), plastics, ceramics, and composites.
- Tooling and Equipment: Familiarize yourself with the cutting tools, machine tools, and equipment used in precision machining.
- Tolerances and Metrology: Gain insights into tolerance requirements and metrology techniques used to measure and verify part dimensions and surface characteristics.
- Design for Manufacturing (DFM): Explore principles of design for manufacturability (DFM) and how they apply to precision machining.
- Quality Assurance: Understand quality control measures and inspection techniques used in precision machining.
- Applications and Industries: Explore the diverse applications of precision machining across industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and tooling.
- Advanced Technologies: Stay informed about advancements in precision machining technology, including automation, robotics, additive manufacturing (3D printing), and advanced materials.
Precision machining and mold technical documents
Other Downloads
- Technical Parameter 3.9 MB
- Technical Drawing 1.8 MB
