Blow Mold Engineering
Breathing Life into Designs. Embrace efficiency and creativity with our Blow Molds, sculpting solutions that inspire and captivate.
Blow Mold
What is Blow Mold?
Blow molding is a manufacturing process that creates hollow plastic parts by blowing air or gas into a mold cavity filled with molten plastic. As the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold is opened to reveal the finished part. This method is commonly used for producing bottles, containers, and other hollow plastic products.
Precision Injection Mold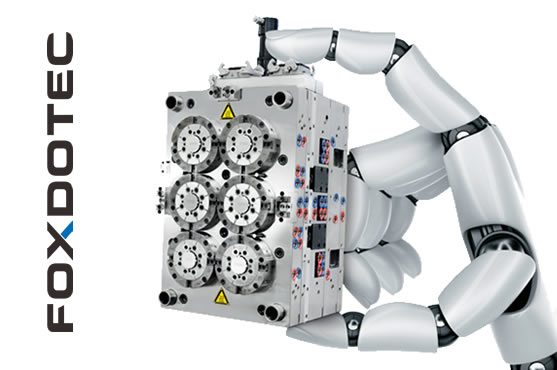


What is Blow Molding Process?
Blow Molding Process
Blow molding is a manufacturing process used to create hollow plastic parts, such as bottles and containers. Here's a detailed overview of the process:
- Extrusion of Parison: The process begins with the extrusion of a tube of molten plastic called a parison. The parison is extruded vertically between two halves of a mold.
- Mold Closure: Once the parison reaches the desired length, the mold closes around it. The mold typically consists of two halves, and it is designed to create the desired shape of the final product.
- Blow Molding: Compressed air is then blown into the parison, causing it to expand and take the shape of the mold cavity. The pressure of the air forces the plastic to conform to the mold's shape, creating a hollow part with a consistent wall thickness.
- Cooling: After the part has been formed, it is allowed to cool and solidify while still inside the mold. Cooling may be accelerated by circulating water or air through the mold.
- Ejection: Once the part has cooled sufficiently, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. In some cases, excess plastic, known as flash, may need to be trimmed from the part.
- Final Inspection: The finished parts undergo inspection to ensure they meet quality standards before being packaged for shipment.
Blow molding is a versatile process suitable for producing a wide range of plastic products, including bottles, containers, and automotive components. Its ability to produce hollow parts with complex geometries and uniform wall thickness makes it a popular choice in various industries.
CNC Machining
CNC machining is a computer-controlled manufacturing process that utilizes pre-programmed software to dictate the movement of machinery and tools. This technology enables the precise cutting, drilling, and shaping of materials such as metal, plastic, and wood to create intricate components with high accuracy and consistency.
Read More
Precision Grinding
Precision grinding is a manufacturing process that involves the removal of material using abrasives to achieve extremely tight tolerances and surface finishes. used to produce components with intricate shapes, precise dimensions, and smooth surfaces. Precision grinding techniques include cylindrical grinding, surface grinding, and internal grinding.
Read More
Electrical Discharge Machining
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a non-traditional machining process that utilizes electrical discharges to erode material from a workpiece. It is particularly useful for machining complex shapes and hardened materials that are difficult to machine with conventional methods. EDM can achieve high precision and surface quality.
Read MorePrecision machining and manufacturing involve the use of advanced techniques and equipment to produce highly accurate and intricate components with tight tolerances. It requires expertise in machining processes, material properties, and quality control methods to ensure the production of high-quality parts for various industries.
Key Aspects of Understanding Injection Molds
- Design Principles: Understand the principles of injection mold design, including considerations for part geometry, material flow, cooling, and ejection.
- Materials and Construction: Explore the materials commonly used in injection mold construction, such as tool steel, aluminum, and beryllium copper.
- Manufacturing Techniques: Gain insights into the manufacturing processes used to produce injection molds, including machining, EDM, and CNC milling.
- Mold Maintenance and Repair: Learn about the importance of mold maintenance and preventive maintenance schedules to ensure the longevity and performance of injection molds.
- Tooling Standards and Regulations: Familiarize yourself with industry standards and regulations related to injection mold design and manufacturing.
- Advanced Technologies: Stay informed about advancements in injection mold technology, such as rapid prototyping, additive manufacturing (3D printing), and simulation software.
- Cost Considerations: Gain insights into the cost factors associated with injection mold production and learn about strategies for cost optimization.
- Case Studies and Best Practices: Study real-world examples of successful injection mold projects across various industries.
Key Aspects of Understanding Precision Machining
- Processes and Techniques: Explore the various precision machining processes and techniques, including turning, milling, drilling, grinding, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and others.
- Materials: Learn about the different types of materials commonly machined using precision techniques, such as metals (e.g., aluminum, steel, titanium), plastics, ceramics, and composites.
- Tooling and Equipment: Familiarize yourself with the cutting tools, machine tools, and equipment used in precision machining.
- Tolerances and Metrology: Gain insights into tolerance requirements and metrology techniques used to measure and verify part dimensions and surface characteristics.
- Design for Manufacturing (DFM): Explore principles of design for manufacturability (DFM) and how they apply to precision machining.
- Quality Assurance: Understand quality control measures and inspection techniques used in precision machining.
- Applications and Industries: Explore the diverse applications of precision machining across industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and tooling.
- Advanced Technologies: Stay informed about advancements in precision machining technology, including automation, robotics, additive manufacturing (3D printing), and advanced materials.
Precision machining and mold technical documents
Other Downloads
- Technical Parameter 3.9 MB
- Technical Drawing 1.8 MB
